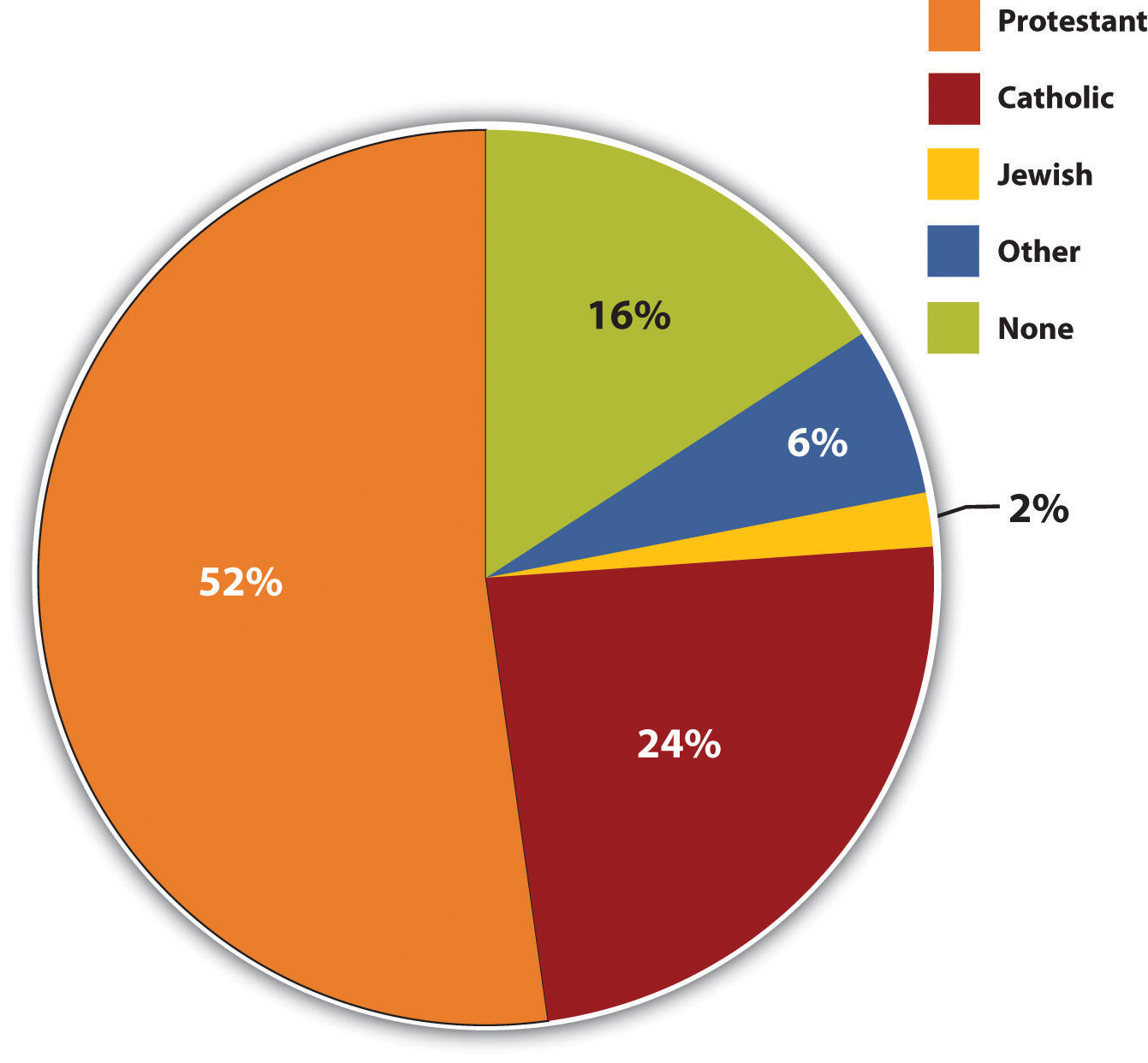
Catholicism is one of the most widely practiced religions in the world, with over 1.3 billion adherents globally. It is a branch of Christianity, and those who practice Catholicism belong to the Christian religion. Catholicism is not just a religious practice but a way of life for millions of people, encompassing spiritual beliefs, traditions, and cultural influences. Understanding Catholicism and its place within Christianity is essential for gaining a deeper appreciation of its history, teachings, and global impact.
Christianity, as a whole, is divided into several denominations, with Catholicism being one of the largest and most influential. The Catholic Church traces its origins to the teachings of Jesus Christ and the apostles, and it has played a pivotal role in shaping Western civilization. This article will explore the core beliefs of Catholicism, its historical roots, and its significance within the broader Christian faith.
Whether you are a practicing Catholic, someone exploring Christianity, or simply curious about world religions, this guide will provide you with valuable insights. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how Catholicism fits into the Christian tradition and why it remains a vital part of the global religious landscape.
Read also:Best Desi Recipes For My Desinet
Table of Contents
- What is Catholicism?
- Historical Roots of Catholicism
- Core Beliefs of Catholicism
- Catholicism and Christianity: How Are They Connected?
- Catholicism vs. Other Christian Denominations
- The Global Influence of Catholicism
- The Cultural Impact of Catholicism
- Key Practices and Traditions in Catholicism
- Contemporary Issues in Catholicism
- Conclusion
What is Catholicism?
Catholicism is a major branch of Christianity that emphasizes the teachings of Jesus Christ as interpreted by the Catholic Church. The word "Catholic" comes from the Greek word "katholikos," which means "universal." This reflects the Church's mission to spread the Gospel to all people, regardless of culture, language, or geography.
At the heart of Catholicism is the belief in the Holy Trinity—God the Father, Jesus Christ the Son, and the Holy Spirit. Catholics also believe in the authority of the Pope, who is considered the spiritual leader of the Church and the successor of Saint Peter, one of Jesus' apostles. The Catholic Church operates under a hierarchical structure, with bishops, priests, and deacons serving as key figures in its administration.
One of the distinguishing features of Catholicism is its sacramental system. Catholics believe in seven sacraments, which are sacred rituals that convey divine grace. These include Baptism, Confirmation, Eucharist, Reconciliation, Anointing of the Sick, Holy Orders, and Matrimony. These sacraments play a central role in the spiritual lives of Catholics and are seen as essential for salvation.
Historical Roots of Catholicism
The roots of Catholicism can be traced back to the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, who lived in the 1st century CE. According to Christian tradition, Jesus appointed Peter as the leader of his apostles, saying, "You are Peter, and on this rock I will build my Church." This statement is often cited as the foundation of the Catholic Church's hierarchical structure.
After Jesus' crucifixion and resurrection, his apostles spread his teachings throughout the Roman Empire. Over time, the early Christian communities began to organize themselves under the leadership of bishops. The Bishop of Rome, who later became known as the Pope, gradually emerged as the central authority figure in the Western Church.
The Great Schism of 1054 marked a significant turning point in the history of Christianity. This event led to the division between the Roman Catholic Church in the West and the Eastern Orthodox Church in the East. Despite this split, Catholicism continued to grow and expand, particularly in Europe, where it became deeply intertwined with political and cultural life.
Read also:Corpse Husband Face The Mystery Behind The Masked Voice
Core Beliefs of Catholicism
Catholicism is built on a foundation of core beliefs that distinguish it from other Christian denominations. These beliefs are outlined in the Nicene Creed, a statement of faith that is recited during Mass. Below are some of the key tenets of Catholicism:
- Belief in the Holy Trinity: Catholics believe in one God who exists in three persons: the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
- The Authority of the Pope: The Pope is considered the Vicar of Christ on Earth and has supreme authority over the Church.
- The Sacraments: Catholics believe that the seven sacraments are essential for spiritual growth and salvation.
- Original Sin: According to Catholic teaching, all humans are born with original sin, which is washed away through Baptism.
- The Resurrection of Jesus: Catholics believe that Jesus rose from the dead and ascended into heaven, offering the promise of eternal life to believers.
These beliefs are supported by centuries of theological reflection and are reinforced through the Church's teachings, traditions, and liturgical practices.
Scripture and Tradition
In addition to the Bible, Catholics rely on Sacred Tradition as a source of divine revelation. Sacred Tradition refers to the teachings and practices passed down through the Church from the time of the apostles. Together, Scripture and Tradition form the basis of Catholic doctrine.
Catholicism and Christianity: How Are They Connected?
Catholicism is a branch of Christianity, and those who practice Catholicism belong to the Christian religion. Christianity itself is divided into three main branches: Catholicism, Protestantism, and Eastern Orthodoxy. While these branches share many core beliefs, such as the divinity of Jesus Christ and the importance of the Bible, they differ in their interpretations of doctrine and practice.
One of the key distinctions between Catholicism and other Christian denominations is its emphasis on tradition and authority. Catholics believe that the Pope and the Magisterium (the teaching authority of the Church) have the final say in matters of faith and morals. This contrasts with Protestant denominations, which often emphasize the authority of Scripture alone (sola scriptura).
Another important difference is the role of the sacraments. While most Christian denominations recognize two sacraments—Baptism and the Eucharist—Catholics believe in seven sacraments, each of which is seen as a means of receiving God's grace.
Catholicism vs. Other Christian Denominations
While Catholicism is the largest Christian denomination, it is not the only one. Protestantism, which emerged during the Reformation in the 16th century, represents a diverse array of denominations, including Lutheranism, Calvinism, Anglicanism, and Baptism. These denominations often differ in their beliefs about church governance, the role of tradition, and the interpretation of Scripture.
Eastern Orthodoxy, on the other hand, shares many similarities with Catholicism but differs in its liturgical practices and theological emphases. For example, Eastern Orthodox Christians reject the authority of the Pope and place greater emphasis on mysticism and theosis (the process of becoming united with God).
Despite these differences, all Christian denominations share a common commitment to the teachings of Jesus Christ and the pursuit of a relationship with God.
The Global Influence of Catholicism
Catholicism has had a profound impact on global history, culture, and society. From its role in the spread of education and healthcare to its influence on art, music, and literature, the Catholic Church has left an indelible mark on the world.
One of the most significant contributions of Catholicism is its emphasis on social justice. The Church has been at the forefront of efforts to combat poverty, promote peace, and advocate for human rights. Encyclicals such as Pope Leo XIII's "Rerum Novarum" and Pope Francis' "Laudato Si'" have addressed issues such as economic inequality, environmental stewardship, and the dignity of work.
Today, Catholicism continues to thrive in regions such as Latin America, Africa, and the Philippines, where it plays a central role in the lives of millions of people. The Church's global presence is reflected in its network of schools, hospitals, and charitable organizations, which serve people of all faiths and backgrounds.
The Cultural Impact of Catholicism
Catholicism has shaped the cultural landscape of many countries, influencing everything from art and architecture to literature and music. Some of the world's most iconic landmarks, such as the Vatican City, St. Peter's Basilica, and the Sistine Chapel, are testaments to the Church's rich artistic heritage.
In literature, Catholic themes and motifs have inspired countless works, from Dante's "Divine Comedy" to Flannery O'Connor's short stories. Similarly, Catholicism has had a profound impact on music, giving rise to genres such as Gregorian chant, sacred polyphony, and contemporary Christian music.
Festivals and Traditions
Catholicism is also known for its vibrant festivals and traditions, which bring communities together to celebrate their faith. Some of the most important Catholic holidays include Christmas, Easter, and Pentecost. These celebrations often involve special liturgies, processions, and feasts, creating a sense of unity and shared purpose among believers.
Key Practices and Traditions in Catholicism
The Catholic faith is characterized by a rich tapestry of practices and traditions that reflect its deep spiritual roots. These practices are designed to help believers grow closer to God and live out their faith in everyday life.
One of the most important practices in Catholicism is attending Mass, which is the central act of worship in the Church. During Mass, Catholics participate in the Eucharist, a sacred ritual in which bread and wine are consecrated and consumed as the body and blood of Christ.
Another key practice is prayer, which is seen as a way of communicating with God. Catholics often engage in both personal and communal prayer, using traditional prayers such as the Our Father, the Hail Mary, and the Rosary.
Devotions
Devotions are another important aspect of Catholic spirituality. These are acts of piety and reverence that go beyond the formal liturgy. Popular devotions include the Stations of the Cross, novenas, and the veneration of saints.
Contemporary Issues in Catholicism
Like any major institution, the Catholic Church faces a range of contemporary challenges. These include declining church attendance in some parts of the world, debates over social issues such as abortion and same-sex marriage, and scandals involving clergy misconduct.
Despite these challenges, the Church remains a powerful force for good in the world. Under the leadership of Pope Francis, the Catholic Church has sought to address these issues through dialogue, reform, and a renewed focus on compassion and inclusivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Catholicism is a vital branch of Christianity that has shaped the spiritual, cultural, and social lives of millions of people around the world. Those who practice Catholicism belong to the Christian religion, and their faith is rooted in the teachings of Jesus Christ and the traditions of the Catholic Church.
From its historical roots to its global influence, Catholicism continues to play a significant role in the lives of believers and non-believers alike. By understanding its core beliefs, practices, and traditions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for its enduring legacy and relevance in today's world.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this article in the comments below. If you found this guide helpful, please consider sharing it with others or exploring more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of world religions.