Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Moderate Political Ideology?
- Characteristics of Moderate Political Ideology
- Historical Perspective
- Moderate Political Ideology in Modern Politics
- Advantages and Challenges of Moderate Political Ideology
- Case Studies of Moderate Political Leaders
- Data and Statistics on Moderate Political Ideology
- Criticisms and Misconceptions
- The Future of Moderate Political Ideology
- Conclusion
Moderate political ideology serves as a bridge between opposing extremes, offering balanced solutions to complex societal issues. In a world increasingly polarized by divisive politics, the role of moderation has become more critical than ever. This ideology emphasizes compromise, pragmatism, and a willingness to consider multiple perspectives, making it a cornerstone of democratic governance. As societies grapple with challenges like economic inequality, climate change, and social justice, understanding moderate political ideology is essential for fostering unity and progress.
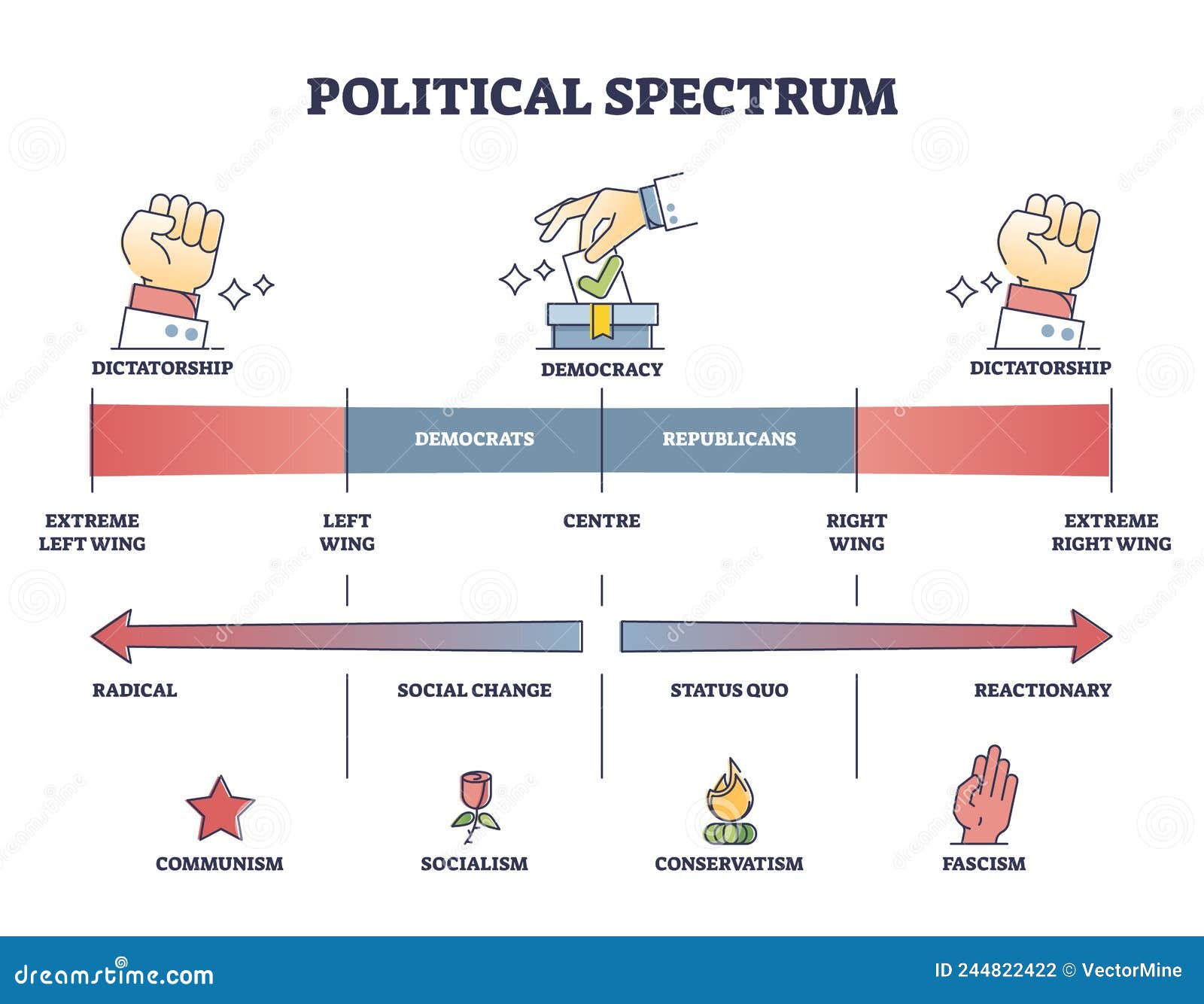
At its core, moderate political ideology rejects rigid dogma and instead prioritizes practical, evidence-based solutions. This approach is particularly relevant in today's fast-paced, interconnected world, where decisions must often be made in the face of uncertainty. By avoiding the extremes of left-wing or right-wing ideologies, moderates aim to create policies that are inclusive and sustainable, addressing the needs of diverse populations without alienating any particular group.
Read also:Dredd The Ultimate Urban Judge Of Justice
The importance of moderate political ideology extends beyond policy-making. It influences how individuals engage with their communities, how leaders navigate crises, and how nations interact on the global stage. This article delves into the nuances of moderate political ideology, exploring its characteristics, historical roots, modern applications, and future prospects. By the end of this comprehensive guide, readers will have a deeper understanding of why moderation matters and how it can shape a better future.
What is Moderate Political Ideology?
Moderate political ideology represents a centrist approach to governance and decision-making, characterized by a willingness to embrace compromise and adaptability. Unlike ideologies that adhere strictly to specific doctrines or principles, moderate political ideology prioritizes pragmatism over ideology. It seeks to balance competing interests and perspectives, often acting as a stabilizing force in politically charged environments. This approach is particularly valuable in addressing issues where no single solution satisfies all stakeholders.
One of the defining features of moderate political ideology is its rejection of extremism. While left-wing ideologies might emphasize equality and social justice, and right-wing ideologies focus on individual liberty and tradition, moderates aim to integrate the strengths of both perspectives. This balance allows them to craft policies that are both progressive and pragmatic, addressing immediate needs without sacrificing long-term stability. For example, a moderate approach to healthcare reform might combine public funding with private innovation, ensuring access while maintaining efficiency.
Another key aspect of moderate political ideology is its emphasis on evidence-based decision-making. Moderates prioritize data and research over rigid adherence to ideological principles. This approach enables them to adapt to changing circumstances and emerging challenges, such as technological advancements or global crises. By remaining open to new information and perspectives, moderates can navigate complex issues with flexibility and creativity, making them well-suited to address the dynamic nature of modern governance.
Characteristics of Moderate Political Ideology
Moderate political ideology is defined by several key characteristics that distinguish it from more rigid ideological frameworks. One of the most prominent traits is its commitment to compromise. Moderates understand that in a diverse society, no single group can monopolize the truth or dictate solutions. Instead, they advocate for collaborative decision-making that incorporates multiple viewpoints, fostering inclusivity and reducing polarization.
Another hallmark of moderate political ideology is its pragmatism. Unlike ideologies driven by abstract principles, moderates focus on practical outcomes. They prioritize what works in real-world scenarios over what aligns with ideological purity. This pragmatic approach often involves incremental reforms rather than sweeping changes, ensuring that policies are both feasible and sustainable. For instance, a moderate approach to climate change might involve incentivizing renewable energy adoption while gradually phasing out fossil fuels, balancing environmental goals with economic realities.
Read also:Best Desi Recipes For My Desinet
Moderate political ideology also emphasizes adaptability. In a rapidly changing world, rigid ideologies can become outdated or counterproductive. Moderates remain open to new ideas, technologies, and methodologies, allowing them to address emerging challenges effectively. This adaptability extends to their willingness to revise policies based on feedback and evidence, ensuring that governance remains responsive to the needs of society. By embracing change while maintaining core values, moderates can navigate the complexities of modern governance with resilience and foresight.
Historical Perspective
The roots of moderate political ideology can be traced back to the Enlightenment era, a period marked by the rise of rationalism and the questioning of absolute authority. Thinkers like John Locke and Montesquieu laid the groundwork for moderation by advocating for balanced governance and the separation of powers. These ideas influenced the development of democratic systems, where moderation became a key principle for preventing tyranny and ensuring stability.
During the 20th century, moderate political ideology gained prominence as a response to the rise of totalitarian regimes. Leaders like Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States and Konrad Adenauer in post-war Germany exemplified moderation by rejecting extremism while addressing pressing societal issues. Roosevelt's New Deal, for example, combined elements of capitalism and social welfare, creating a pragmatic framework for economic recovery. Similarly, Adenauer's policies balanced traditional values with modernization, fostering reconciliation and rebuilding after World War II.
In more recent history, moderate political ideology has played a crucial role in resolving conflicts and fostering cooperation. The peace process in Northern Ireland, for instance, was driven by moderate leaders who prioritized dialogue over division. By focusing on shared goals and mutual respect, these leaders were able to bridge longstanding divides and achieve lasting peace. Such historical examples underscore the enduring relevance of moderation in addressing complex societal challenges.
Moderate Political Ideology in Modern Politics
In today's polarized political landscape, moderate political ideology serves as a vital counterbalance to extremism. As political discourse becomes increasingly divisive, moderates play a crucial role in fostering dialogue and finding common ground. This approach is particularly evident in legislative bodies, where moderates often act as mediators, bridging the gap between opposing factions and enabling bipartisan cooperation.
One of the most significant contributions of moderate political ideology in modern politics is its focus on evidence-based policy-making. In an era of misinformation and political polarization, moderates prioritize data and research to inform decisions. This approach ensures that policies are grounded in reality rather than ideology, enhancing their effectiveness and credibility. For example, moderate politicians have been instrumental in advancing evidence-based responses to public health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, by supporting measures like mask mandates and vaccination campaigns based on scientific consensus.
Another important aspect of moderate political ideology in modern politics is its emphasis on inclusivity. Moderates recognize the importance of representing diverse perspectives and addressing the needs of all constituents, not just those aligned with their political base. This inclusive approach fosters trust and legitimacy, making governance more responsive and equitable. By prioritizing collaboration over confrontation, moderates can build coalitions that transcend traditional political divides, paving the way for meaningful progress on issues like climate change, economic inequality, and social justice.
Examples of Moderate Political Leaders
Several contemporary political leaders exemplify the principles of moderate political ideology. For instance, Angela Merkel, the former Chancellor of Germany, was widely regarded as a moderate leader who prioritized pragmatism and stability. Her leadership during the European financial crisis and the refugee crisis demonstrated a balanced approach that combined compassion with practicality. Similarly, Joe Biden, the current President of the United States, has positioned himself as a moderate leader focused on unity and bipartisanship, emphasizing the need to "lower the temperature" in American politics.
Advantages and Challenges of Moderate Political Ideology
Moderate political ideology offers several advantages that make it particularly appealing in complex, diverse societies. One of the primary benefits is its ability to foster compromise and collaboration. By prioritizing dialogue and mutual respect, moderates can bridge divides and build consensus, even in highly polarized environments. This approach not only enhances the legitimacy of governance but also ensures that policies are inclusive and sustainable, addressing the needs of all stakeholders rather than favoring specific groups.
Another advantage of moderate political ideology is its adaptability. In a rapidly changing world, rigid ideologies can become outdated or counterproductive. Moderates, however, remain open to new ideas and evidence, allowing them to address emerging challenges effectively. This flexibility enables them to craft innovative solutions that balance competing interests, such as combining economic growth with environmental protection or integrating technological advancements with ethical considerations. By remaining responsive to changing circumstances, moderates can navigate the complexities of modern governance with resilience and foresight.
Challenges Faced by Moderate Political Ideology
Despite its many advantages, moderate political ideology also faces significant challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the perception of moderation as indecisiveness or lack of conviction. In highly polarized environments, moderates are often criticized for being "wishy-washy" or failing to take a firm stance on key issues. This perception can undermine their credibility and make it difficult to mobilize support, particularly in electoral contexts where voters may gravitate toward more ideologically defined candidates.
Another challenge is the difficulty of maintaining balance in an increasingly polarized political landscape. As political discourse becomes more extreme, moderates often find themselves caught between opposing factions, struggling to find common ground. This can lead to accusations of betrayal from both sides, making it challenging to build lasting coalitions. Additionally, the rise of social media and echo chambers has amplified polarization, making it harder for moderates to reach audiences and promote their message effectively.
Case Studies of Moderate Political Leaders
Several political leaders have successfully embodied moderate political ideology, achieving significant impact through their balanced and pragmatic approaches. One notable example is Nelson Mandela, whose leadership during South Africa's transition from apartheid to democracy exemplified moderation. Mandela prioritized reconciliation over retribution, working to unite a deeply divided nation through dialogue and forgiveness. His ability to bridge racial and political divides made him a symbol of hope and resilience, demonstrating the transformative power of moderate leadership.
Another prominent case study is Angela Merkel, whose tenure as Chancellor of Germany was marked by pragmatic decision-making and crisis management. Merkel's leadership during the European financial crisis and the refugee crisis showcased her commitment to evidence-based policy and inclusive governance. By balancing economic stability with humanitarian concerns, she earned international respect and admiration, reinforcing the value of moderate political ideology in addressing complex challenges.
Biography and Data of Nelson Mandela
| Full Name | Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | July 18, 1918 |
| Date of Death | December 5, 2013 |
| Nationality | South African |
| Political Affiliation | African National Congress (ANC) |
| Key Achievements | Ending apartheid, promoting reconciliation, serving as South Africa's first Black president |
Data and Statistics on Moderate Political Ideology
Understanding the prevalence and impact of moderate political ideology requires examining relevant data and statistics. According to a 2022 Pew Research Center study, approximately 34% of Americans identify as politically moderate, highlighting the significant presence of this ideology in one of the world's most polarized democracies. This figure underscores the enduring appeal of moderation, even in environments dominated by partisan divides.
Another key statistic comes from a global survey conducted by the World Values Survey Association, which found that countries with higher levels of political moderation tend to exhibit greater social cohesion and economic stability. For instance, nations like Canada and Germany, known for their centrist political cultures, consistently rank high in quality-of-life indices, including healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability. These findings suggest a correlation between moderate political ideology and positive societal outcomes.
Impact of Moderate Policies on Public Trust
Data also reveals the impact of moderate political ideology