The Khalistan movement has been a topic of significant debate and controversy, particularly in the context of India's geopolitical landscape. At the heart of this discussion lies the concept of the Khalistan map, a representation of a proposed independent Sikh state. This article delves into the intricacies of the Khalistan map, exploring its historical roots, political implications, and the ongoing discourse surrounding it. Whether you're a history enthusiast, a political analyst, or simply curious, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights into the subject.
The idea of Khalistan has its roots in the 20th century, when Sikh communities in India began advocating for greater autonomy and recognition of their cultural identity. Over the decades, the movement has evolved, with some factions calling for complete independence. The Khalistan map is often used as a visual tool to illustrate the geographical boundaries of this proposed state. While the map remains a point of contention, understanding its origins and implications is crucial for grasping the complexities of the movement.
In this article, we will explore the Khalistan map in detail, examining its historical background, the political and social factors driving the movement, and the challenges it poses to India's unity. By the end of this piece, you will have a clear understanding of why the Khalistan map continues to be a topic of global interest and how it fits into the broader narrative of self-determination movements worldwide.
Read also:Layla Deline Unveiling The Rising Star In The Entertainment World
Table of Contents
- Historical Background of the Khalistan Movement
- What is the Khalistan Map?
- Geographical Boundaries and Regions
- Political Implications of the Khalistan Map
- International Perspective on Khalistan
- Challenges to India's Unity and Sovereignty
- Key Figures in the Khalistan Movement
- Data and Biodata of Prominent Leaders
- Statistics and Trends in Support of Khalistan
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Historical Background of the Khalistan Movement
The Khalistan movement emerged as a response to perceived marginalization of the Sikh community in post-independence India. During the mid-20th century, Sikhs were a significant minority in Punjab, a region with a rich cultural and religious heritage. The demand for greater autonomy and recognition of Sikh identity gained momentum during the 1940s and 1950s, as the community sought to preserve its distinct traditions and practices.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the movement took a more radical turn, with some groups advocating for the creation of an independent Sikh state. This period was marked by political unrest, violence, and clashes between the Indian government and Khalistan supporters. The infamous Operation Blue Star in 1984, which involved a military assault on the Golden Temple in Amritsar, further escalated tensions and fueled the movement's momentum.
Today, the Khalistan movement exists in various forms, with supporters spread across India and the global Sikh diaspora. While some factions continue to push for independence, others focus on cultural preservation and political representation within the Indian framework. Understanding this historical context is essential for comprehending the significance of the Khalistan map.
What is the Khalistan Map?
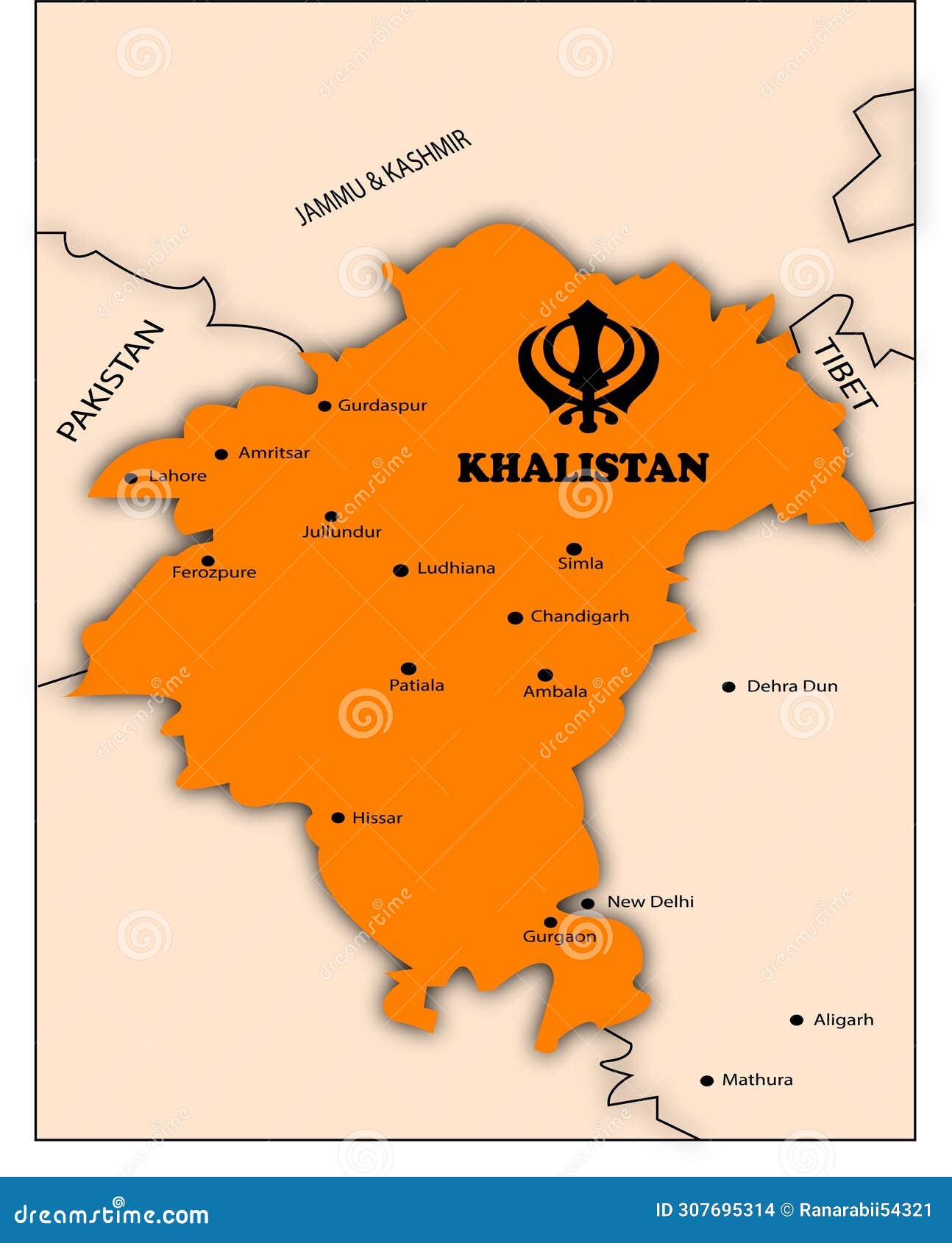
The Khalistan map is a visual representation of the proposed boundaries of an independent Sikh state. It typically includes the Indian state of Punjab, along with parts of neighboring regions such as Haryana and Himachal Pradesh. The map is often used by Khalistan supporters to symbolize their vision of a sovereign Sikh nation, free from Indian governance.
While the exact boundaries of the Khalistan map vary depending on the source, the core idea remains consistent: the creation of a separate state where Sikhs can exercise self-determination and preserve their cultural heritage. The map is not just a geographical tool but also a political statement, reflecting the aspirations of those who support the movement.
It is important to note that the Khalistan map is not recognized by any international body or government. The Indian government strongly opposes the idea, viewing it as a threat to national unity and sovereignty. Despite this, the map continues to be a powerful symbol for Khalistan supporters, particularly in the diaspora.
Read also:Salt Trick For Men In Shower Enhance Your Shower Experience
Geographical Boundaries and Regions
The proposed geographical boundaries of Khalistan are often depicted as encompassing the Indian state of Punjab, which is considered the cultural and religious heartland of the Sikh community. Punjab is home to the Golden Temple in Amritsar, the holiest site in Sikhism, making it a focal point for the movement.
Key Regions in the Khalistan Map
- Punjab: The central region of the proposed state, known for its fertile agricultural land and vibrant Sikh culture.
- Haryana: Parts of this neighboring state are sometimes included due to their significant Sikh population.
- Himachal Pradesh: Certain areas with historical ties to Sikh rulers and communities are also considered.
While the map is largely symbolic, it highlights the regions where Sikh influence is most prominent. These areas are characterized by their distinct language, Punjabi, and a shared cultural identity that sets them apart from other parts of India.
Political Implications of the Khalistan Map
The Khalistan map has far-reaching political implications, both within India and on the global stage. Domestically, the map is seen as a challenge to India's territorial integrity and a potential catalyst for further fragmentation. The Indian government has consistently rejected the idea, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a unified nation.
Internationally, the Khalistan movement has garnered attention from human rights organizations and foreign governments. Some countries, particularly those with large Sikh populations, have expressed concerns about the treatment of Sikhs in India. However, no country has formally recognized the Khalistan map or supported the idea of an independent Sikh state.
The political discourse surrounding the Khalistan map is complex, involving issues of identity, autonomy, and governance. While some view it as a legitimate expression of self-determination, others see it as a threat to national stability. This dichotomy underscores the challenges of addressing such movements in a democratic framework.
International Perspective on Khalistan
The international community's response to the Khalistan movement has been mixed. On one hand, there is sympathy for the Sikh community's desire for cultural preservation and political representation. On the other hand, there is reluctance to support any movement that could destabilize a major global power like India.
In countries like Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States, where significant Sikh populations reside, the Khalistan map is often discussed in political and social circles. These communities have organized protests, rallies, and campaigns to raise awareness about their cause. However, their efforts have sometimes led to tensions with local governments, which are wary of supporting movements that could strain diplomatic relations with India.
From a global perspective, the Khalistan movement is part of a broader trend of self-determination movements. While some have succeeded in achieving independence, others remain unresolved. The Khalistan map serves as a reminder of the ongoing struggle for identity and recognition in an increasingly interconnected world.
Challenges to India's Unity and Sovereignty
The Khalistan movement poses several challenges to India's unity and sovereignty. One of the primary concerns is the potential for increased regionalism and separatism. If the movement gains traction, it could inspire other groups within India to demand greater autonomy or independence, further fragmenting the nation.
Another challenge is the impact on India's international reputation. The movement has drawn criticism from human rights organizations, which accuse the Indian government of suppressing dissent and violating the rights of Sikhs. While the government denies these allegations, the perception of India as a repressive state could undermine its standing on the global stage.
Finally, the Khalistan movement has economic implications. Punjab is one of India's most agriculturally productive states, and any disruption to its stability could have ripple effects on the national economy. Ensuring peace and prosperity in the region is therefore a priority for the Indian government.
Key Figures in the Khalistan Movement
The Khalistan movement has been shaped by several key figures who have played pivotal roles in its development. These individuals have advocated for Sikh rights, organized protests, and raised awareness about the cause. Below are some of the most prominent leaders associated with the movement.
Data and Biodata of Prominent Leaders
| Name | Date of Birth | Role in Movement | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale | 1947 | Spiritual Leader | Advocated for Sikh rights and led protests in Punjab. |
| Gurpatwant Singh Pannun | 1968 | Legal Advocate | Filed petitions for Khalistan's independence at international forums. |
| Hardeep Singh Nijjar | 1975 | Activist | Organized global campaigns to raise awareness about Khalistan. |
These leaders, among others, have contributed to the movement's growth and visibility. Their efforts have kept the issue of Khalistan alive in public discourse, both in India and abroad.
Statistics and Trends in Support of Khalistan
While it is difficult to quantify support for the Khalistan movement, certain statistics and trends provide insights into its reach and influence. According to surveys conducted among Sikh communities in the diaspora, a significant percentage express sympathy for the cause, although support for independence varies widely.
- Global Sikh Population: Approximately 25 million Sikhs worldwide, with significant populations in India, Canada, the UK, and the US.
- Diaspora Support: An estimated 30-40% of Sikhs in the diaspora support some form of autonomy or independence.
- Online Engagement: Social media platforms have become a key tool for Khalistan supporters, with millions of followers across various channels.
These statistics highlight the movement's global reach and the role of digital platforms in amplifying its message. However, they also underscore the challenges of achieving widespread support within India, where the movement remains a contentious issue.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The Khalistan map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a symbol of the aspirations and struggles of the Sikh community. While the movement for an independent Sikh state remains controversial, understanding its historical and political context is essential for engaging in informed discussions about India's future.
As we have explored in this article, the Khalistan movement is shaped by complex factors, including identity, autonomy, and governance. Whether you agree or disagree with the idea of Khalistan, it is important to approach the topic with an open mind and a commitment to dialogue.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this article in the comments section below. Have you heard about the Khalistan map before? What are your views on the movement? Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site to learn more about related topics. Together, let's foster a deeper understanding of the world around us.