Table of Contents
Introduction
How long does it take to become a psychiatrist? This is a common question for those who are considering a career in mental health. Psychiatry is a rewarding yet demanding field that requires years of education, training, and dedication. If you're passionate about understanding the human mind and helping people overcome mental health challenges, this career path may be perfect for you. However, it’s essential to understand the time commitment and steps involved before embarking on this journey.
Becoming a psychiatrist involves a structured process that includes undergraduate studies, medical school, residency training, and licensing. Each step is crucial in shaping a competent and qualified mental health professional. In this article, we will explore the timeline, requirements, and challenges of becoming a psychiatrist. Whether you're a high school student or a career changer, this guide will provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision.
Psychiatry is not just about diagnosing and treating mental illnesses; it’s about improving the quality of life for individuals and their families. With the increasing awareness of mental health issues, the demand for skilled psychiatrists is higher than ever. Let’s dive into the details of what it takes to become a psychiatrist and how you can prepare for this fulfilling career.
Read also:Corpse Husband Face The Mystery Behind The Masked Voice
What is a Psychiatrist?
A psychiatrist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing, treating, and preventing mental health disorders. Unlike psychologists, psychiatrists can prescribe medications and utilize a combination of therapy and medical interventions to address mental health issues. They work with patients of all ages, from children to the elderly, and their expertise spans a wide range of conditions, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and more.
Psychiatrists often collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as psychologists, social workers, and primary care physicians, to provide comprehensive care. Their role is critical in the healthcare system, as mental health is closely linked to physical health. By addressing psychological and emotional issues, psychiatrists help patients lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Below is a table summarizing the key differences between psychiatrists and psychologists:
| Aspect | Psychiatrist | Psychologist |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Medical degree (MD or DO) | Doctoral degree (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) |
| Prescription Authority | Yes | No |
| Treatment Approach | Medication, therapy, medical interventions | Therapy, counseling, behavioral interventions |
| Focus | Biological, psychological, and social factors | Behavioral and emotional factors |
Educational Pathway to Becoming a Psychiatrist
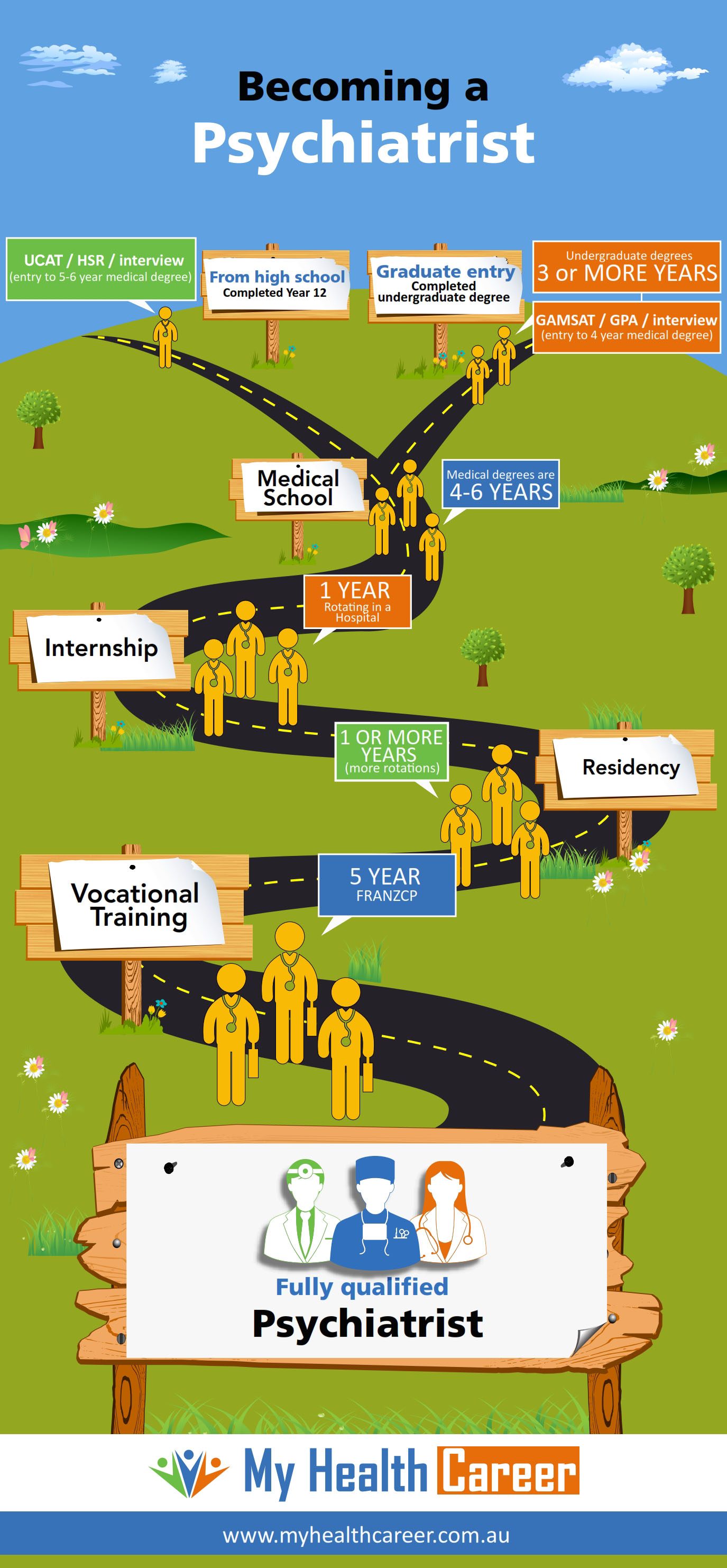
The journey to becoming a psychiatrist is a long and structured process. It typically takes about 12 years of education and training after high school. This includes four years of undergraduate studies, four years of medical school, and four years of residency training. Below, we will break down each step in detail to help you understand the timeline and requirements.
Undergraduate Education
The first step in becoming a psychiatrist is completing a bachelor's degree. While there is no specific major required, most aspiring psychiatrists choose fields such as psychology, biology, chemistry, or pre-med. These majors provide a strong foundation in the sciences, which is essential for medical school.
- Coursework: Focus on biology, chemistry, physics, and psychology courses.
- GPA: Maintain a high GPA to increase your chances of getting into medical school.
- MCAT: Prepare for and take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT), which is a requirement for medical school applications.
During your undergraduate years, it’s also important to gain experience in healthcare settings. Volunteering at hospitals or clinics, shadowing psychiatrists, and participating in research projects can strengthen your application and provide valuable insights into the field.
Read also:Aurora Belova Unveiling The Enigma Of A Rising Star
Medical School
After completing your undergraduate degree, the next step is attending medical school. Medical school typically lasts four years and is divided into two phases: pre-clinical and clinical.
- Pre-Clinical Phase: The first two years focus on classroom and laboratory work, covering subjects like anatomy, pharmacology, and pathology.
- Clinical Phase: The last two years involve hands-on training in various medical specialties, including psychiatry.
During medical school, students also take the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) or the Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX) to qualify for residency programs. These exams assess a student’s knowledge and readiness to practice medicine.
Residency Training
After graduating from medical school, aspiring psychiatrists must complete a four-year residency program in psychiatry. Residency training provides specialized education and hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders.
- Year 1: Focus on general psychiatry and foundational skills.
- Years 2-3: Gain experience in various settings, such as inpatient, outpatient, and emergency psychiatry.
- Year 4: Specialize in areas of interest, such as child and adolescent psychiatry or addiction psychiatry.
Residency programs also emphasize psychotherapy techniques, medication management, and interdisciplinary collaboration. By the end of the program, residents are well-prepared to practice independently.
Licensing and Certification
Once residency is complete, psychiatrists must obtain a medical license to practice. Licensing requirements vary by state but generally include passing the USMLE or COMLEX and completing residency training. Additionally, many psychiatrists choose to become board-certified by the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN). Board certification demonstrates expertise and commitment to the field.
Here are the key steps for licensing and certification:
- Pass the required licensing exams.
- Apply for a state medical license.
- Complete the board certification process (optional but recommended).
Specializations in Psychiatry
After completing residency, psychiatrists can choose to specialize in a specific area of psychiatry. Specializations require additional training, typically in the form of fellowships, which last one to two years. Some popular specializations include:
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Focuses on diagnosing and treating mental health issues in children and teenagers.
- Addiction Psychiatry: Addresses substance abuse and addiction disorders.
- Geriatric Psychiatry: Specializes in mental health care for older adults.
- Forensic Psychiatry: Combines psychiatry with the legal system, often involving court evaluations.
Specializing allows psychiatrists to focus on areas they are passionate about and provide more targeted care to specific populations.
Challenges and Rewards of Being a Psychiatrist
Like any career, psychiatry comes with its own set of challenges and rewards. Understanding these aspects can help you decide if this is the right path for you.
Challenges
- Long Education and Training: The journey to becoming a psychiatrist is lengthy and demanding.
- Emotional Strain: Working with individuals facing mental health challenges can be emotionally taxing.
- Workload: Psychiatrists often have busy schedules, including evenings and weekends.
Rewards
- Impact on Lives: Psychiatrists play a crucial role in improving the mental health and well-being of their patients.
- Job Stability: The demand for mental health professionals is consistently high.
- Personal Growth: The field offers opportunities for continuous learning and professional development.
Career Outlook for Psychiatrists
The career outlook for psychiatrists is promising. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of psychiatrists is projected to grow by 12% from 2022 to 2032, faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by increased awareness of mental health issues and the need for specialized care.
Psychiatrists can work in various settings, including hospitals, private practices, academic institutions, and government agencies. Salaries vary depending on location, experience, and specialization, but the median annual wage for psychiatrists is approximately $220,000.
Conclusion
Becoming a psychiatrist is a long and challenging journey, but it is also incredibly rewarding. With a commitment of about 12 years of education and training, you can make a meaningful impact on the lives of individuals and communities. By understanding the steps involved—undergraduate education, medical school, residency, and licensing—you can better prepare for this fulfilling career.
If you’re passionate about mental health and helping others, psychiatry may be the perfect path for you. Take the first step today by exploring undergraduate programs and gaining experience in healthcare settings. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning about how long it takes to become a psychiatrist, and feel free to leave your thoughts in the comments below!