Fleas are tiny, wingless insects that are notorious for their ability to infest pets and homes, causing discomfort and potential health risks. These pests are not only a nuisance but can also transmit diseases and cause allergic reactions. Many people wonder, "Do fleas live on humans?" This question is particularly important because understanding flea behavior can help you take effective measures to protect yourself and your loved ones. Fleas are primarily associated with animals, but their interactions with humans are worth exploring to ensure a pest-free environment.
Fleas thrive in warm, humid environments and are often found on pets like dogs and cats. However, their ability to jump long distances allows them to move between hosts, including humans. While fleas do not typically live on human skin, they can bite humans and cause itching, rashes, and even infections. This article will delve into the biology of fleas, their behavior, and whether they can live on humans. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to prevent and manage flea infestations.
In the following sections, we will explore the life cycle of fleas, their preferred hosts, and the conditions that make humans vulnerable to flea bites. Additionally, we will provide practical tips for flea prevention and treatment. Whether you’re dealing with a flea problem or simply want to stay informed, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to handle these pesky insects effectively.
Read also:Salt Trick For Men In Shower Enhance Your Shower Experience
Table of Contents
- Understanding Fleas: What Are They?
- The Life Cycle of Fleas
- Preferred Hosts of Fleas
- Do Fleas Live on Humans?
- How Flea Bites Affect Humans
- Health Risks Associated with Fleas
- Preventing Flea Infestations
- Treating Flea Bites and Infestations
- Natural Remedies for Flea Control
- Conclusion: Stay Informed and Protected
Understanding Fleas: What Are They?
Fleas are small, parasitic insects that belong to the order Siphonaptera. They are external parasites, meaning they live on the outside of their hosts, feeding on their blood. Fleas are approximately 1-3 millimeters in length, making them difficult to spot with the naked eye. Their bodies are flattened from side to side, allowing them to move easily through the fur or feathers of their hosts. Fleas are also equipped with powerful legs that enable them to jump up to 200 times their body length.
These pests are most commonly associated with household pets, such as dogs and cats, but they can also infest other animals, including rodents, rabbits, and birds. Fleas thrive in warm, humid environments, which is why they are more prevalent in certain regions and during specific seasons. Their ability to reproduce rapidly makes them a significant challenge to control once an infestation occurs.
Understanding the biology and behavior of fleas is crucial for effective prevention and management. By learning about their life cycle and preferred hosts, you can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of flea infestations in your home and on your pets.
The Life Cycle of Fleas
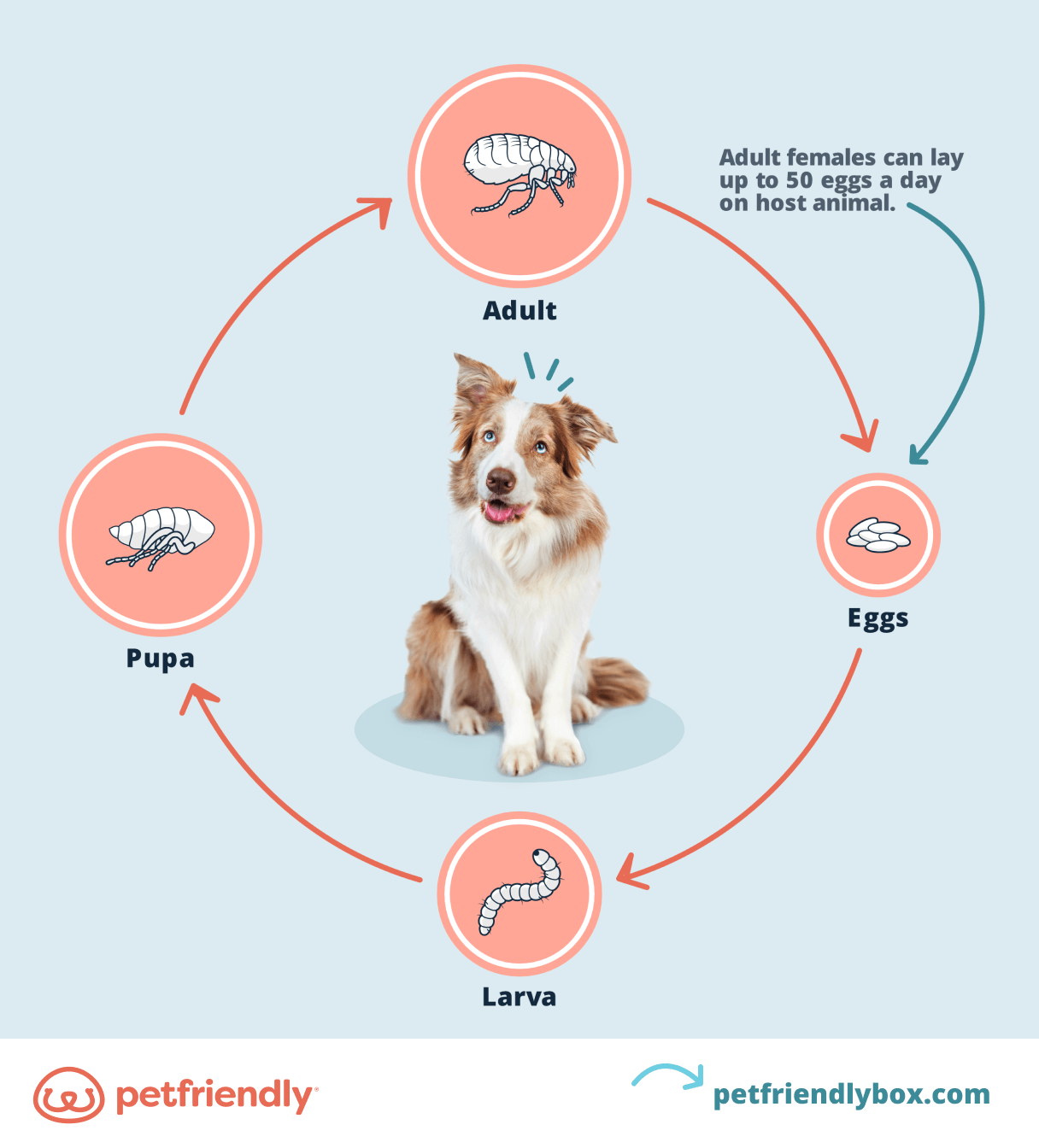
Fleas undergo a four-stage life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. This cycle can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity.
Egg Stage
Female fleas lay eggs on their host, but these eggs often fall off into the surrounding environment, such as carpets, bedding, or furniture. A single female flea can lay up to 50 eggs per day, contributing to the rapid spread of infestations.
Larva Stage
The eggs hatch into larvae within 1-10 days. Flea larvae are small, worm-like creatures that feed on organic debris, including adult flea feces, which contain undigested blood. They avoid light and prefer dark, humid areas.
Read also:Layla Deline Unveiling The Rising Star In The Entertainment World
Pupa Stage
After feeding for about 5-11 days, the larvae spin cocoons and enter the pupal stage. This stage can last from days to months, as the pupae remain dormant until conditions are favorable for adult emergence.
Adult Stage
Once they emerge, adult fleas seek a host to feed on. They can survive for several weeks without a blood meal but will die within a few days if they cannot find a host. Adult fleas are the stage most commonly encountered by humans and pets.
Preferred Hosts of Fleas
Fleas are highly adaptable and can infest a wide range of animals. However, they have preferences based on factors such as body temperature, hair density, and ease of access to blood. The most common hosts for fleas include:
- Dogs and Cats: These pets are the primary hosts for fleas due to their warm bodies and thick fur, which provide an ideal environment for fleas to thrive.
- Rodents: Mice and rats can carry fleas into homes, contributing to infestations.
- Birds: Fleas may infest birds, particularly in outdoor settings.
- Humans: While humans are not the preferred host, fleas can bite humans when their primary hosts are unavailable.
Do Fleas Live on Humans?
Fleas do not typically live on humans because human skin lacks the thick fur or feathers that fleas prefer for protection and reproduction. However, humans can still be bitten by fleas, especially in environments with heavy infestations. Fleas are opportunistic feeders and will target humans if their preferred hosts are unavailable.
Why Fleas Prefer Animals
Fleas are adapted to living on animals with dense fur, which provides them with shelter and a stable environment. Human skin is less suitable for fleas because it lacks the necessary conditions for their survival. Additionally, humans are more likely to notice and remove fleas, making them a less reliable host.
When Fleas Bite Humans
Flea bites on humans often occur on the lower legs and feet, as these areas are closest to the ground where fleas are likely to be found. The bites can cause itching, redness, and swelling, and in some cases, lead to allergic reactions or infections.
How Flea Bites Affect Humans
Flea bites are not only irritating but can also pose health risks. The bites typically appear as small, red bumps, often in clusters or lines. They are most commonly found on the ankles, legs, and feet but can occur anywhere on the body.
Symptoms of Flea Bites
- Itching and irritation
- Red, swollen bumps
- Secondary infections from scratching
- Allergic reactions in sensitive individuals
Treatment for Flea Bites
To relieve the discomfort of flea bites, you can use over-the-counter antihistamines or topical creams. Avoid scratching the bites to prevent infections. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional.
Health Risks Associated with Fleas
Fleas are not just a nuisance; they can also transmit diseases and parasites to humans and animals. Some of the most common health risks associated with fleas include:
- Plague: Fleas can transmit the bacteria that cause plague, a serious and potentially life-threatening disease.
- Murine Typhus: This bacterial infection is spread by fleas and can cause fever, headache, and rash.
- Tapeworms: Fleas can carry tapeworm larvae, which can infect pets and, in rare cases, humans.
- Allergic Dermatitis: Some individuals develop severe allergic reactions to flea bites, leading to intense itching and skin inflammation.
Preventing Flea Infestations
Preventing flea infestations is key to avoiding the discomfort and health risks associated with these pests. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
- Regularly groom and bathe your pets to remove fleas and their eggs.
- Use flea prevention products, such as collars, sprays, or oral medications, recommended by your veterinarian.
- Vacuum your home frequently, paying special attention to carpets, rugs, and furniture.
- Wash pet bedding and household linens in hot water to kill fleas and their eggs.
- Seal cracks and crevices in your home to prevent fleas from entering.
Treating Flea Bites and Infestations
If you or your pets are affected by fleas, prompt treatment is essential to prevent further infestations. Here are some steps you can take:
Treating Flea Bites
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and itching.
- Use over-the-counter creams or ointments to soothe the skin.
- Avoid scratching the bites to prevent infections.
Eliminating Fleas from Your Home
- Use flea sprays or foggers designed for indoor use.
- Wash all fabrics, including bedding and curtains, in hot water.
- Vacuum thoroughly and dispose of the vacuum bag immediately.
- Consult a pest control professional for severe infestations.
Natural Remedies for Flea Control
If you prefer natural solutions, there are several remedies you can try to control fleas:
- Diatomaceous Earth: This natural powder dehydrates fleas and their eggs when sprinkled on carpets and furniture.
- Essential Oils: Oils like lavender, eucalyptus, and cedarwood can repel fleas when used in diffusers or diluted sprays.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Adding a small amount to your pet’s water can help repel fleas.
- Herbal Flea Collars: These collars use natural ingredients to deter fleas without harsh chemicals.
Conclusion: Stay Informed and Protected
Fleas may not live on humans, but their bites can cause significant discomfort and health risks. By understanding their behavior and taking preventive measures, you can protect yourself, your family, and your pets from flea infestations. Regular grooming, cleaning, and the use of flea prevention products are essential steps in maintaining a flea-free environment.
If you suspect a flea problem in your home, act quickly to address the issue. Consult a veterinarian for advice on treating your pets and consider hiring a pest control professional for severe infestations. Share this article with friends and family to help them stay informed about flea prevention and treatment. Together, we can create healthier, pest-free living spaces.