Table of Contents
Introduction
What is the molar mass of CaCO3? This is a question that often arises in chemistry classes and scientific discussions. Calcium carbonate, commonly known as CaCO3, is a compound that plays a vital role in various industries, from construction to healthcare. Understanding its molar mass is essential for students, researchers, and professionals alike.
Calcium carbonate is a naturally occurring compound found in rocks, shells, and even our own bodies. Its molar mass is a fundamental property that helps us calculate how much of the substance is needed in chemical reactions or industrial processes. This article will explore the concept of molar mass, explain how to calculate it for CaCO3, and highlight its importance in both scientific and everyday contexts.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what the molar mass of CaCO3 is, why it matters, and how it is applied in real-world scenarios. Let’s dive in and uncover the science behind this essential compound.
Read also:Aishah Sofey Exploring The Life And Achievements Of A Rising Star
What is CaCO3?
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a chemical compound composed of calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). It is one of the most abundant compounds on Earth and is found in various forms, such as limestone, chalk, and marble. CaCO3 is also a key component of shells, pearls, and even eggshells.
Here are some key facts about CaCO3:
- Chemical formula: CaCO3
- Molar mass: Approximately 100.09 g/mol
- Common uses: Construction, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and more
CaCO3 is classified as a carbonate salt and is known for its versatility. It is used in industries ranging from manufacturing to environmental protection, making it a compound of significant importance.
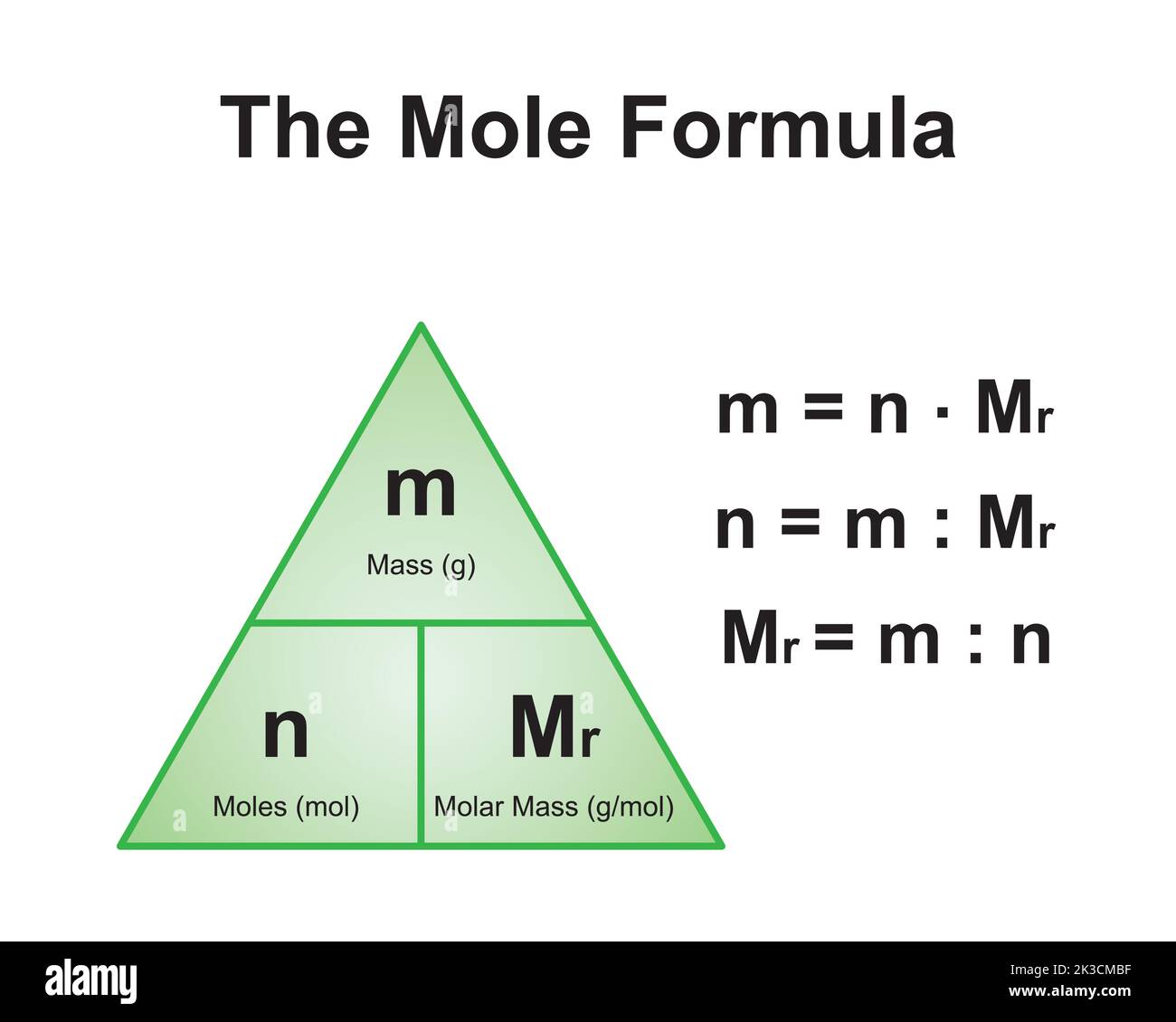
Molar Mass Explained
Molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry that refers to the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a unit of measurement used to express the amount of a substance, and it is equivalent to Avogadro’s number (6.022 × 10²³) of particles, such as atoms or molecules.
The molar mass of a compound is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in its chemical formula. For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is calculated by adding the atomic masses of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
In the case of CaCO3, the molar mass is determined by adding the atomic masses of calcium, carbon, and three oxygen atoms. Understanding this concept is crucial for performing accurate chemical calculations and experiments.
Read also:Elon Musks Children A Comprehensive Look Into The Lives Of The Tech Moguls Offspring
How to Calculate the Molar Mass of CaCO3
To calculate the molar mass of CaCO3, we need to determine the atomic masses of its constituent elements and then sum them up. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Find the atomic mass of calcium (Ca): 40.08 g/mol
- Find the atomic mass of carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
- Find the atomic mass of oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol (since there are three oxygen atoms, multiply by 3)
- Add the values: 40.08 + 12.01 + (16.00 × 3) = 100.09 g/mol
Thus, the molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol. This value is essential for determining how much of the compound is needed in chemical reactions or for preparing solutions.
Why is Accurate Calculation Important?
Accurate calculation of molar mass ensures precision in experiments and industrial processes. For example, in pharmaceuticals, knowing the exact molar mass of CaCO3 is crucial for formulating medications and supplements.
Why is Molar Mass Important?
The molar mass of a compound like CaCO3 is not just a theoretical concept—it has practical applications in various fields. Here are some reasons why understanding molar mass is crucial:
- It helps in determining the amount of substance needed for chemical reactions.
- It is essential for preparing solutions of specific concentrations.
- It aids in quality control and standardization in industries.
For instance, in agriculture, CaCO3 is used to neutralize acidic soils. Knowing its molar mass ensures that the correct amount is applied to achieve the desired pH level.
Applications of CaCO3 in Daily Life
Calcium carbonate has a wide range of applications in various industries. Here are some of its most common uses:
- Construction: Used as a raw material for cement and lime production.
- Agriculture: Acts as a soil conditioner to neutralize acidity.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used as a calcium supplement and antacid.
- Food Industry: Serves as a food additive and preservative.
These applications highlight the versatility of CaCO3 and its importance in both industrial and everyday contexts.
Common Questions About CaCO3 and Molar Mass
Here are some frequently asked questions about CaCO3 and its molar mass:
- What is the molar mass of CaCO3? The molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol.
- Why is CaCO3 important? It is used in industries such as construction, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals.
- How is molar mass calculated? By summing the atomic masses of all atoms in the compound’s chemical formula.
Practical Examples of Using CaCO3
Let’s explore some real-world examples of how CaCO3 is used:
- In construction, CaCO3 is used to make cement and lime, which are essential for building infrastructure.
- In agriculture, it is used to neutralize acidic soils, improving crop yields.
- In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used as a calcium supplement to prevent osteoporosis.
Environmental Impact
CaCO3 also plays a role in environmental protection. For example, it is used in water treatment processes to remove impurities and pollutants.
The Scientific Significance of CaCO3
Calcium carbonate is not just a compound used in industries—it also has significant scientific importance. It is a key component of marine ecosystems, forming the shells and skeletons of many organisms. Additionally, it is used in research to study geological processes and climate change.
Understanding the properties of CaCO3, including its molar mass, contributes to advancements in science and technology. This knowledge helps researchers develop new materials, improve industrial processes, and address environmental challenges.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the question, "What is the molar mass of CaCO3?" and provided a comprehensive guide to understanding this essential compound. We learned that the molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol and that it is calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent elements.
Calcium carbonate is a versatile compound with applications in construction, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and more. Its molar mass is a crucial property that ensures precision in chemical calculations and industrial processes. By understanding the significance of CaCO3 and its molar mass, we can appreciate its role in both scientific and everyday contexts.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. Don’t forget to share this article with others who might find it useful!