Table of Contents
Calcium carbonate, commonly known as CaCO3, is a fundamental compound in chemistry and plays a vital role in various industries and natural processes. Understanding its molar mass is essential for anyone studying chemistry, working in industries that utilize this compound, or simply curious about its properties. The molar mass of CaCO3 in grams is a key concept that helps in quantifying the substance for practical applications.
Have you ever wondered how chemists determine the exact amount of a substance needed for a reaction? The molar mass of CaCO3 is one of the foundational elements in such calculations. This article will delve into the intricacies of CaCO3, explain what molar mass is, and provide a step-by-step guide to calculating the molar mass of CaCO3 in grams. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just someone eager to learn, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
Read also:Girthmaster And Mia Z The Ultimate Guide To Their Collaboration And Impact
By the end of this article, you will not only understand the molar mass of CaCO3 but also appreciate its significance in various fields. From its role in manufacturing to its environmental impact, CaCO3 is more than just a chemical compound—it's a cornerstone of modern science and industry. Let’s explore this fascinating topic together!
What is CaCO3?
Calcium carbonate, or CaCO3, is a chemical compound composed of calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). It is one of the most abundant compounds on Earth and exists in various natural forms, such as limestone, chalk, and marble. Its widespread presence makes it a critical component in numerous applications, from construction materials to dietary supplements.
Here are some key facts about CaCO3:
- Chemical Formula: CaCO3
- Common Forms: Limestone, chalk, marble
- Uses: Construction, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and more
Understanding the properties of CaCO3 is essential for grasping its molar mass and its role in chemical reactions. Let’s now explore what molar mass means and why it is so important.
Molar Mass Explained
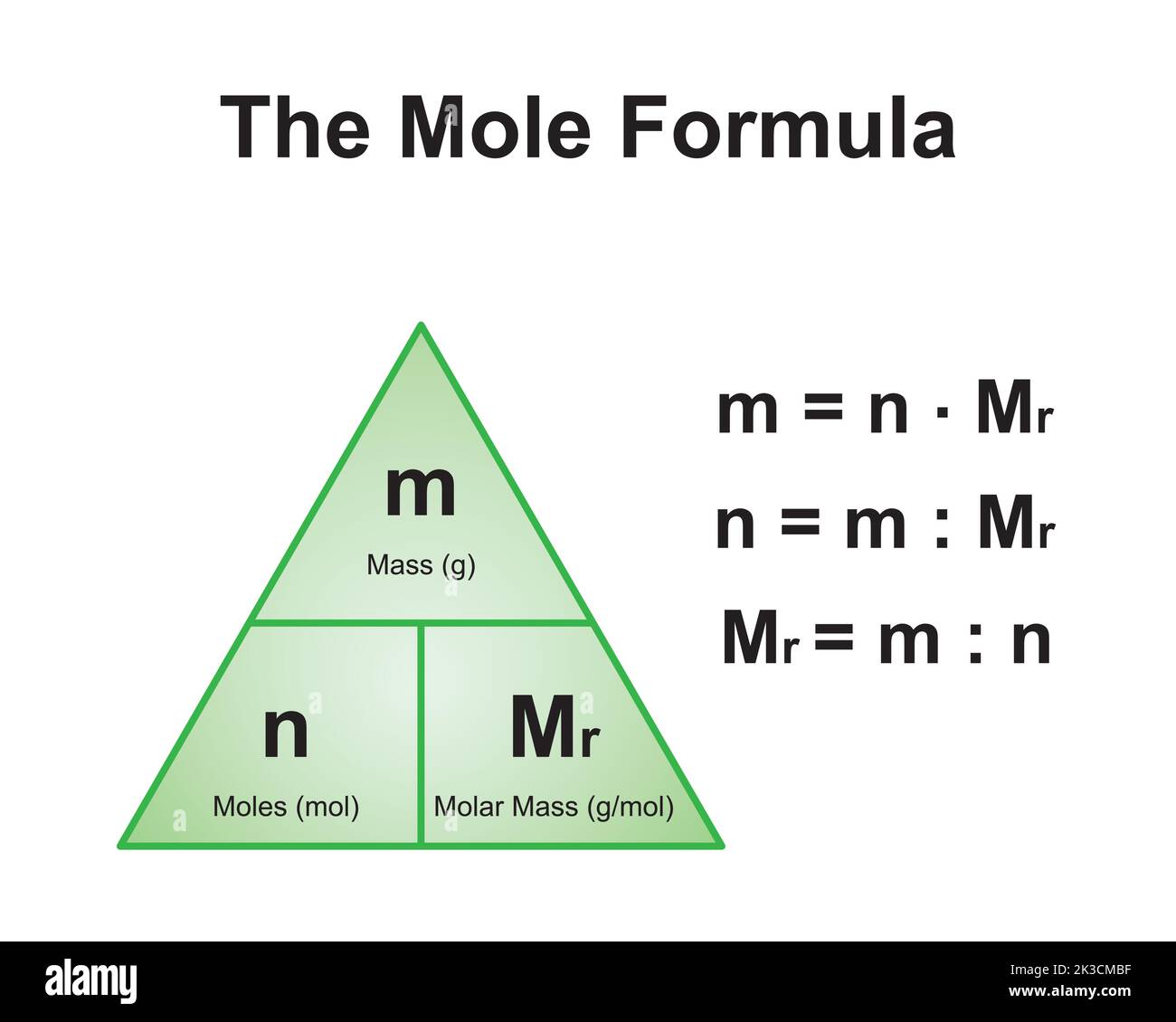
Molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry that refers to the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole is a unit used to quantify the amount of a substance, and it is defined as the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12. The molar mass of a compound is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound.
For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is calculated as follows:
Read also:Avery Leigh A Comprehensive Guide To The Rising Star
- Hydrogen (H): 1.008 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Total: (2 × 1.008) + 16.00 = 18.016 g/mol
Understanding molar mass is crucial because it allows chemists to determine the exact amount of a substance needed for reactions, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in experiments and industrial processes.
Calculating the Molar Mass of CaCO3
Now that we understand what molar mass is, let’s calculate the molar mass of CaCO3 step by step. To do this, we need to know the atomic masses of calcium (Ca), carbon (C), and oxygen (O). These values can be found on the periodic table:
- Calcium (Ca): 40.08 g/mol
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
The chemical formula of CaCO3 indicates that it contains one calcium atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms. Therefore, the molar mass of CaCO3 is calculated as follows:
- Calcium: 40.08 g/mol
- Carbon: 12.01 g/mol
- Oxygen: (3 × 16.00) = 48.00 g/mol
- Total: 40.08 + 12.01 + 48.00 = 100.09 g/mol
Thus, the molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol. This value is essential for determining the amount of CaCO3 needed in various applications, from laboratory experiments to industrial processes.
Why is the Molar Mass of CaCO3 Important?
The molar mass of CaCO3 is critical for stoichiometric calculations, which involve determining the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. For example, in the reaction between CaCO3 and hydrochloric acid (HCl), knowing the molar mass of CaCO3 allows chemists to calculate the exact amount of HCl required for complete neutralization.
Applications of CaCO3
Calcium carbonate has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Construction: CaCO3 is a primary component of cement and is used in the production of lime and limestone.
- Agriculture: It is used as a soil conditioner to neutralize acidic soils and provide essential calcium for plant growth.
- Pharmaceuticals: CaCO3 is a common ingredient in antacids and calcium supplements.
- Paper and Plastics: It is used as a filler to enhance the properties of paper and plastic products.
These applications highlight the versatility of CaCO3 and underscore the importance of understanding its molar mass for precise usage.
Importance of CaCO3 in Chemistry
In the field of chemistry, CaCO3 serves as a model compound for studying various chemical reactions and processes. Its decomposition into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) is a classic example of a thermal decomposition reaction:
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
This reaction is widely used in industries such as cement production and metallurgy. Understanding the molar mass of CaCO3 is essential for optimizing these processes and ensuring efficient resource utilization.
CaCO3 in Laboratory Experiments
In educational settings, CaCO3 is often used in laboratory experiments to teach students about stoichiometry, acid-base reactions, and gas evolution. Its well-defined molar mass makes it an ideal compound for these demonstrations.
Environmental Significance of CaCO3
Calcium carbonate plays a crucial role in the environment, particularly in marine ecosystems. It is a primary component of shells and skeletons of marine organisms such as corals, mollusks, and some plankton species. The formation and dissolution of CaCO3 in the oceans are influenced by factors such as pH levels and temperature, making it a key indicator of ocean health.
Here are some environmental impacts of CaCO3:
- Ocean Acidification: Increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere lead to ocean acidification, which affects the ability of marine organisms to form CaCO3 structures.
- Carbon Sequestration: CaCO3 formation in marine environments contributes to the natural sequestration of carbon dioxide.
Understanding the molar mass of CaCO3 is essential for studying these environmental processes and developing strategies to mitigate their impacts.
Common Questions About CaCO3
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about CaCO3 and its molar mass:
What is the significance of the molar mass of CaCO3?
The molar mass of CaCO3 is crucial for calculating the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions, ensuring accuracy in experiments and industrial processes.
How is CaCO3 used in everyday life?
CaCO3 is used in a variety of products, including antacids, dietary supplements, paper, plastics, and construction materials.
What are the environmental impacts of CaCO3?
CaCO3 plays a vital role in marine ecosystems and is affected by environmental factors such as ocean acidification and climate change.
Practical Examples of Using CaCO3
Here are some practical examples of how CaCO3 is used in real-world scenarios:
- Antacid Tablets: CaCO3 is a key ingredient in antacids, where it reacts with stomach acid to neutralize excess acidity.
- Construction Materials: It is used in the production of cement and lime, which are essential for building infrastructure.
- Water Treatment: CaCO3 is used to adjust the pH of water and remove impurities.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and importance of CaCO3 in various industries and applications.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the molar mass of CaCO3 in grams and its significance in chemistry, industry, and the environment. We learned that the molar mass of CaCO3 is approximately 100.09 g/mol, a value that is essential for accurate calculations in chemical reactions and industrial processes. From its role in construction materials to its environmental impact, CaCO3 is a compound that touches many aspects of our lives.
We encourage you to share your thoughts or questions about CaCO3 in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this knowledge. For more informative articles on chemistry and related topics, explore our website and stay updated with the latest insights!